CNC (Computer Numerical Control) cutting is a versatile and precise manufacturing process used across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, mold-making, and general metalworking. The choice of material plays a crucial role in determining machining efficiency, tool wear, surface finish, and production costs.
Materials used in CNC cutting can be categorized into metals, plastics, composites, and specialty materials, each with unique characteristics and machining challenges. Below, we explore the most common materials used in CNC cutting and their applications.
1. Metals: The Backbone of CNC Machining
Metals are widely used in CNC cutting due to their high strength, durability, and heat resistance. They are essential in industries that require precision, reliability, and wear resistance.
(1) Aluminum and Its Alloys
- Why It’s Used: Lightweight, easy to machine, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective.
- Common Grades: 6061, 7075, 2024 (used in aerospace, automotive, and electronics).
- Challenges: Produces long, continuous chips that require proper chip control.
(2) Steel and Stainless Steel
- Why It’s Used: High strength, wear resistance, and good thermal properties.
- Common Grades:
- Mild Steel (1018, 1045) – Used in general manufacturing.
- Tool Steel (D2, H13, M2) – Ideal for molds, dies, and cutting tools.
- Stainless Steel (304, 316, 410) – Corrosion-resistant, used in medical and food industries.
- Challenges: Higher tool wear; requires carbide tools with CVD/PVD coatings for efficiency.
(3) Titanium and Its Alloys
- Why It’s Used: Extremely strong, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant.
- Common Grades: Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) – Used in aerospace, medical implants, and marine applications.
- Challenges: Difficult to machine due to its toughness and low thermal conductivity. Requires high-performance carbide tools.
(4) Brass and Copper
- Why It’s Used: Excellent electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and machinability.
- Common Grades:
- Brass (C36000) – Used in electrical components and fittings.
- Copper (C101, C110) – Used in electrical and heat transfer applications.
- Challenges: Soft materials that can generate built-up edges (BUE), requiring sharp cutting tools.
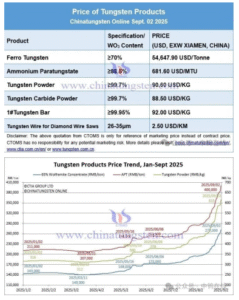
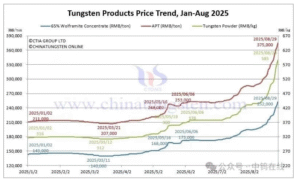
(5) Tungsten and Tungsten Carbide
- Why It’s Used: Extreme hardness and wear resistance.
- Common Grades: Tungsten Carbide (WC-Co) – Used in cutting tools and wear parts.
- Challenges: Requires diamond or CBN (cubic boron nitride) tools for machining.
2. Plastics: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Plastics are commonly used in CNC cutting for lightweight, non-conductive, and corrosion-resistant applications. They are widely used in medical, automotive, electronics, and consumer goods.
(1) ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
- Why It’s Used: High impact strength, easy to machine, and cost-effective.
- Applications: Used in prototypes, automotive parts, and consumer electronics.
- Challenges: Can melt if cut too aggressively.
(2) Acrylic (PMMA)
- Why It’s Used: Transparent, lightweight, and impact-resistant.
- Applications: Used in displays, optical lenses, and medical devices.
- Challenges: Prone to cracking and chipping if not machined with the right speeds and feeds.
(3) Nylon and Delrin (Acetal)
- Why It’s Used: Strong, wear-resistant, and self-lubricating.
- Applications: Used in gears, bushings, and high-friction parts.
- Challenges: Generates static electricity and requires sharp tools to prevent burrs.
(4) PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
- Why It’s Used: High strength, temperature and chemical resistance.
- Applications: Used in aerospace, medical implants, and automotive.
- Challenges: Expensive material requiring precise cutting conditions.
3. Composites: High-Performance, Low Weight
Composites are engineered materials that combine fibers (carbon, glass) with resin (epoxy, polyester). They are widely used in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods due to their high strength-to-weight ratio.
(1) Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP)
- Why It’s Used: Extremely lightweight, strong, and fatigue-resistant.
- Applications: Used in aircraft, race cars, bicycles, and medical devices.
- Challenges: Highly abrasive on cutting tools, requiring diamond-coated tools.
(2) Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP)
- Why It’s Used: Cost-effective, corrosion-resistant, and durable.
- Applications: Used in boats, wind turbine blades, and chemical tanks.
- Challenges: Brittle, prone to delamination, and requires slow feed rates.
4. Specialty Materials: High-Precision Applications
Certain industries require specialty materials that offer unique properties for extreme environments.
(1) Ceramics
- Why It’s Used: High temperature and wear resistance.
- Applications: Used in cutting tools, aerospace coatings, and biomedical implants.
- Challenges: Very brittle, requires diamond grinding tools.
(2) Superalloys (Inconel, Hastelloy, Monel, Waspaloy)
- Why It’s Used: High heat and corrosion resistance in extreme environments.
- Applications: Used in jet engines, turbines, and nuclear reactors.
- Challenges: Difficult to machine, requires high-speed carbide tools with PVD coatings.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for CNC Cutting
The selection of CNC materials depends on:
✔ Strength, hardness, and machinability requirements
✔ Heat and corrosion resistance needs
✔ Application-specific performance (wear, conductivity, weight)
At Zhuzhou Zhirong Advanced Materials Co., Ltd., we provide high-performance tungsten carbide cutting tools designed for machining metals, plastics, composites, and superalloys. Our products, including CVD/PVD-coated carbide inserts, end mills, drills, and carbide rods, ensure superior wear resistance and precision.
For expert consultation on choosing the best cutting tools for CNC applications, contact us at:
crystalyuan@zrzhirong.com
www.zhirongcarbide.com