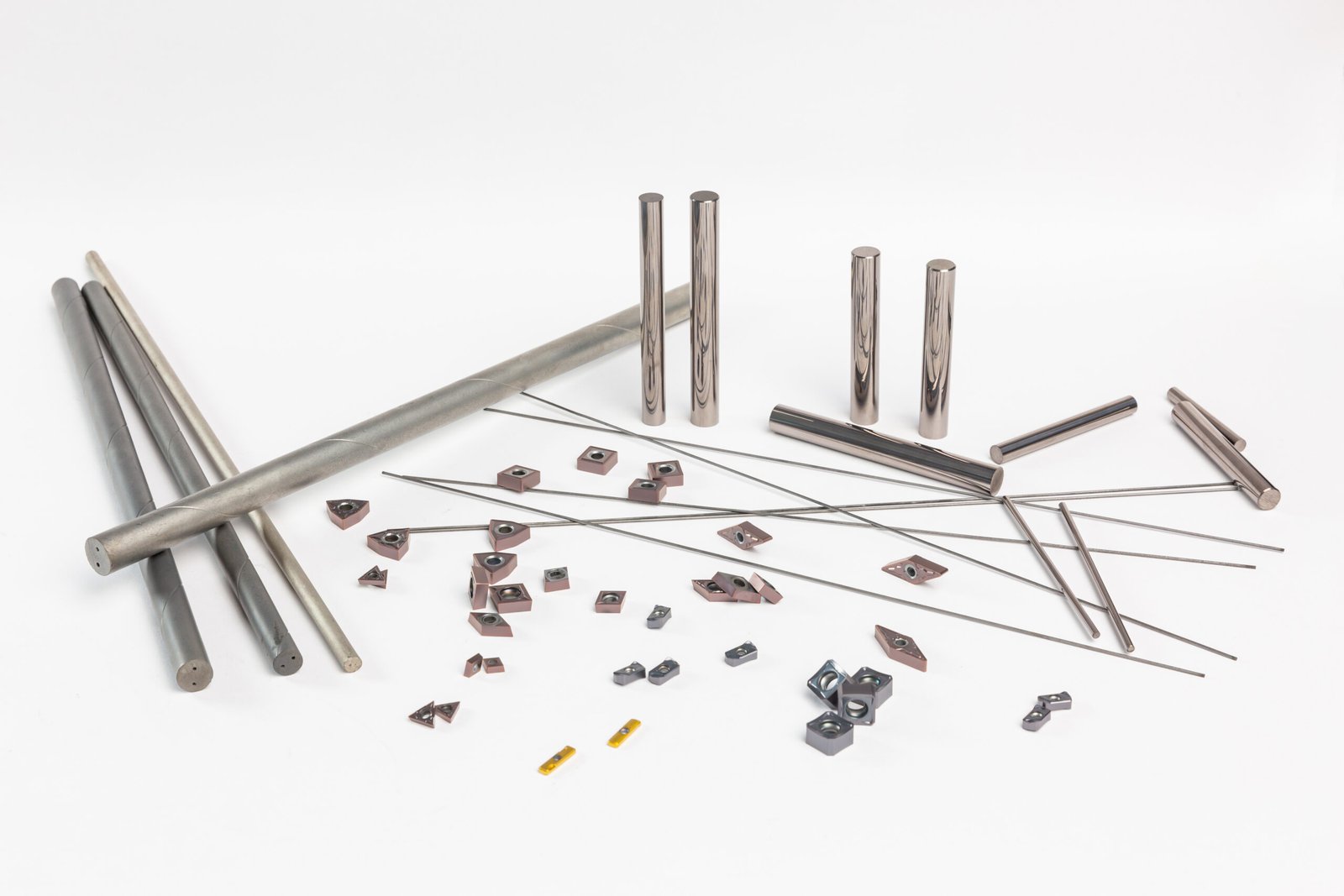
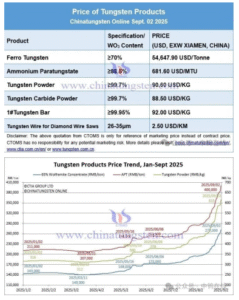
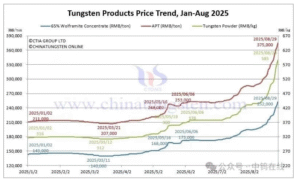
Silicon carbide (SiC) and tungsten carbide (WC) are both extremely hard and wear-resistant materials used in various industrial applications. However, each material has unique properties, making them better suited for specific purposes. The choice between silicon carbide and tungsten carbide depends on factors such as hardness, toughness, thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and application requirements.
Below, we provide a detailed comparison to help manufacturers, engineers, and tool buyers determine the best material for their needs.
1. Hardness and Wear Resistance
Hardness is one of the most critical factors when selecting a material for cutting tools, mechanical seals, or wear-resistant components.
- Silicon carbide (SiC) is significantly harder than tungsten carbide, with a Mohs hardness of 9.5, close to diamond (Mohs 10). This extreme hardness gives SiC excellent abrasion resistance and longevity in high-friction environments.
- Tungsten carbide (WC) has a Mohs hardness of around 9, making it one of the hardest metals available. While slightly softer than silicon carbide, tungsten carbide is still highly wear-resistant and commonly used in cutting tools.
Conclusion: Silicon carbide is harder, making it superior for applications requiring extreme wear resistance.
2. Toughness and Impact Resistance
Although silicon carbide is harder, it is also brittle, meaning it is more prone to cracking or shattering under impact.
- Tungsten carbide has higher toughness, meaning it can withstand heavy impacts and mechanical stress without breaking. This makes WC ideal for cutting tools, drilling, and high-impact applications such as mining and machining.
- Silicon carbide, while highly wear-resistant, is brittle and more likely to fracture under sudden force or impact. It is better suited for low-impact, high-friction environments such as mechanical seals and bearings.
Conclusion: Tungsten carbide is tougher, making it better for high-impact applications like machining and drilling.
3. Thermal Conductivity and High-Temperature Performance
Both materials perform well under high temperatures, but silicon carbide has better thermal conductivity and heat resistance than tungsten carbide.
- Silicon carbide has excellent thermal conductivity and can withstand temperatures above 1,600°C, making it ideal for high-temperature applications such as heat exchangers and furnace components.
- Tungsten carbide has a lower thermal conductivity and can handle temperatures up to 1,400°C, but it retains strength better under extreme mechanical loads.
Conclusion: Silicon carbide is better for high-temperature applications, while tungsten carbide is better for structural applications under mechanical stress.
4. Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
For applications involving chemical exposure, acids, or seawater, corrosion resistance is an important factor.
- Silicon carbide is highly resistant to corrosion, making it an excellent choice for chemical processing, pumps, and marine environments.
- Tungsten carbide is corrosion-resistant but can degrade in highly acidic or oxidizing environments.
Conclusion: Silicon carbide is the better choice for corrosive environments.
5. Industrial Applications: Where Each Material Excels
When to Use Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Best for high-temperature and corrosion-resistant applications
Ideal for mechanical seals, bearings, heat exchangers, and semiconductors
Excellent for abrasive wear resistance without impact loads
Used in ceramic components, refractory materials, and armor plating
When to Use Tungsten Carbide (WC)
Best for cutting tools, drilling, and machining applications
Ideal for mining tools, wear parts, and industrial equipment
Excellent for high-stress and impact-resistant applications
Used in milling inserts, turning inserts, and industrial dies
6. Cost and Availability
Both materials are expensive, but tungsten carbide is generally more widely available due to its extensive use in cutting tools and industrial applications. Silicon carbide, being a specialty material, is often more costly for precision applications.
- Silicon carbide is more expensive for specialized applications such as semiconductors and chemical processing.
- Tungsten carbide has a lower cost per unit and is widely available, making it more cost-effective for industrial tools.
Conclusion: Tungsten carbide is generally more cost-effective and readily available for industrial applications.
Final Verdict: Which One is Better?
The best material depends on the application.
- For extreme hardness, wear resistance, and high-temperature applications → Choose Silicon Carbide (SiC)
- For toughness, impact resistance, and industrial cutting tools → Choose Tungsten Carbide (WC)
- For corrosion resistance and chemical exposure → Choose Silicon Carbide (SiC)
- For cost-effective machining and industrial applications → Choose Tungsten Carbide (WC)
At Zhuzhou Zhirong Advanced Materials Co., Ltd., we specialize in high-performance tungsten carbide cutting tools, including turning inserts, milling inserts, end mills, and drills. Our tungsten carbide products are made from 100% virgin tungsten carbide powder, ensuring superior wear resistance, toughness, and long tool life.
For expert recommendations on carbide cutting tools, contact us at crystalyuan@zrzhirong.com or visit www.zhirongcarbide.com. We also provide free samples for testing to ensure the best performance for your applications.