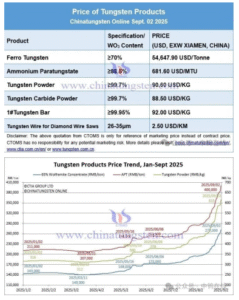
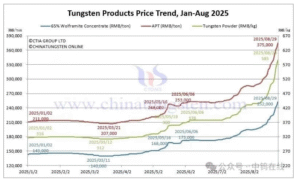
ZhuZhou Zhirong Advanced Material Co., Ltd
Choosing the right turning insert can be confusing, especially with so many types and designations. Misidentifying inserts can lead to poor performance, shortened tool life, and costly mistakes. This guide will walk you through the basics of turning insert identification so you can choose the right tool with confidence.
Turning inserts are identified through a standardized coding system that specifies shape, clearance angle, tolerance, cutting edge, and size. Each letter and number in the code provides crucial information about the insert's characteristics and best use. Understanding these codes allows machinists to select the right insert for their specific application.
Let’s break down turning insert identification so you can make the best choice for your machining needs.
What Do the Letters and Numbers on Turning Inserts Mean?
Turning inserts are labeled with a specific code, typically consisting of letters and numbers in a sequence (such as CNMG 120408). Each character in this code represents a unique feature of the insert, including its shape, clearance angle, and size. Here’s a breakdown:
Shape
The first letter indicates the shape of the insert, such as:
- C: Rhombic with 80° angle
- S: Square
- D: Rhombic with 55° angle
- T: Triangle
- W: Trigon (a rounded triangle shape)
This shape defines the type of cuts and the strength of the insert, with higher angles providing more strength and durability.
Clearance Angle
The second letter shows the clearance or relief angle:
- N: 0° (no clearance)
- P: 11°
- C: 7°
Clearance angle affects chip control and surface finish, with higher angles typically used for finishing.
Tolerance
The third character (also a letter) describes the manufacturing tolerance:
- M: Medium tolerance (often used for roughing)
- G: Ground precision tolerance (for finishing)
Cutting Edge Style
The fourth letter refers to the type of edge, such as:
- G: Ground edge (for precision cutting)
- H: High-positive rake angle (for finishing cuts)
Insert Size
Following the letters, the first set of numbers refers to the insert’s size, usually the diameter or inscribed circle length, in millimeters.
Thickness
The next number denotes the thickness of the insert.
Corner Radius
The last number refers to the corner radius, affecting durability and surface finish.
Understanding these specifications allows machinists to select the correct insert based on the workpiece material and cutting requirements.
Why Is Carbide insertsIt Important to Choose the Right Turning Insert?
Choosing the right turning insert affects the quality of the finish, tool life, and efficiency of the machining process. Using an incorrect insert can lead to:
- Poor Surface Finish: The wrong insert can cause rough surfaces or chatter.
- Reduced Tool Life: Incompatible inserts wear out faster, increasing costs.
- Inefficient Chip Removal: Poorly matched insert geometry can cause chip buildup, impacting productivity.
Selecting the right insert type for your material and application helps ensure smooth, cost-effective operations.
What Are the Common Shapes of Turning Inserts?
Turning inserts come in various shapes, each suited for different types of operations. Common shapes include:
- C (80° Diamond): Most popular shape, offering balance between strength and versatility.
- T (Triangle): Provides multiple cutting edges but less strength than diamond inserts.
- D (55° Diamond): Suited for precision finishing but more delicate than 80° inserts.
- S (Square): Great for roughing; square inserts offer strong corners.
- R (Round): Ideal for heavy cuts and high-feed applications due to their robustness.
Each shape has distinct strengths based on cutting requirements and the desired finish.
How Do I Select a Turning Insert for Different Materials?
Material type plays a significant role in insert selection. Common considerations include:
- Steel: Carbide inserts with PVD or CVD coatings work well for steel. A tougher insert with a sharp cutting edge can handle varying hardness.
- Stainless Steel: High heat and resistance require inserts with a positive rake angle and strong edge retention.
- Cast Iron: Choose inserts with durable coatings that resist chipping; typically, inserts with lower clearance angles work well.
- Aluminum: Use uncoated or polished inserts with a high rake angle for a smooth finish and optimal chip flow.
Matching the insert material, coating, and geometry to the workpiece ensures optimal tool performance and durability.
What Are the Different Types of Insert Coatings?
Coatings enhance insert performance by increasing wear resistance, durability, and heat dissipation. Common coatings include:
- CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition): Excellent for steel and cast iron, providing toughness at high temperatures.
- PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition): Best for stainless steel and hard materials where sharp cutting edges are needed.
- Uncoated Carbide: Typically used for softer materials like aluminum to avoid chemical reactions.
Selecting the correct coating extends tool life and reduces tool wear, especially in high-speed applications.
How Can I Maximize Tool Life When Using Turning Inserts?
To extend tool life, follow these best practices:
- Optimize Cutting Parameters: Use appropriate speeds and feeds based on material and insert specifications.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep inserts clean and replace them at the first sign of wear.
- Use the Correct Coolant: Ensure adequate cooling for better surface finish and longevity.
- Consider the Depth of Cut: Avoid overloading the insert by using depth cuts within its tolerance range.
These practices will help reduce tooling costs and increase efficiency.
Conclusion
Turning insert identification is essential for optimizing machining performance. With the right selection and careful handling, you can achieve excellent surface finishes and prolong tool life in your turning operations.