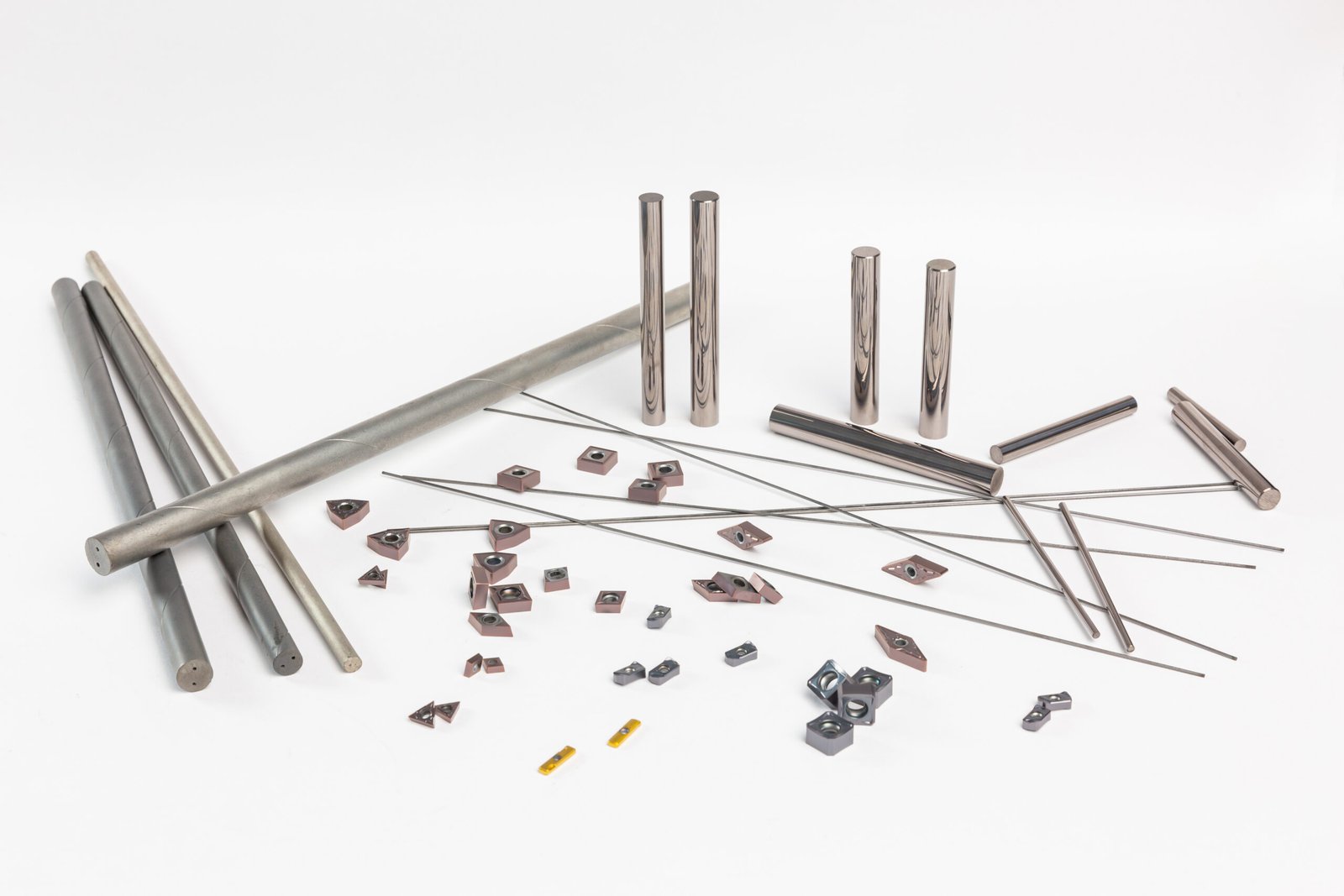
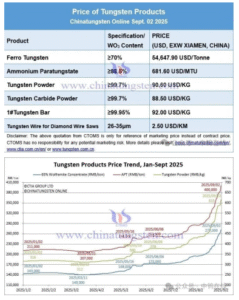
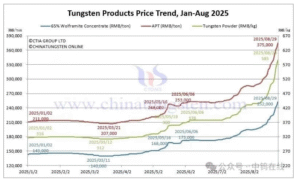
In modern CNC machining and metal cutting applications, cutting tool selection plays a critical role in determining machining efficiency, surface finish, and overall production cost. Among the most widely used cutting inserts are cermet and carbide inserts, both offering unique advantages depending on the material being machined and the application requirements.
Understanding the key differences between cermet and carbide inserts can help manufacturers choose the right tool for their specific needs, optimizing both tool life and cutting performance. Below, we analyze their composition, properties, advantages, and ideal use cases.
1. Composition and Material Properties
The primary difference between cermet and carbide inserts lies in their material composition.
- Carbide Inserts: Made from tungsten carbide (WC) as the base material, combined with a binder metal such as cobalt (Co) or nickel (Ni). Tungsten carbide provides extreme hardness, while the metal binder adds toughness, making carbide inserts highly resistant to wear and impact.
- Cermet Inserts: A combination of ceramic (cer) and metal (met) materials, primarily composed of titanium carbide (TiC) or titanium nitride (TiN) with a small amount of metal binders like nickel or cobalt. This composition gives cermet inserts a unique balance between ceramic hardness and metal toughness.
Because of these material differences, carbide inserts are generally tougher and better suited for heavy-duty machining, while cermet inserts excel in high-speed finishing applications due to their excellent wear resistance and reduced friction.
2. Performance and Cutting Characteristics
Due to their different compositions, cermet and carbide inserts perform differently in machining operations:
- Wear Resistance and Tool Life:
- Cermet inserts have superior resistance to built-up edge (BUE) formation and exhibit excellent wear resistance, making them ideal for high-speed finishing and continuous cutting applications.
- Carbide inserts, while also highly durable, may experience faster wear at high temperatures, but their greater toughness allows them to withstand interrupted cuts and heavier cutting loads.
- Surface Finish and Cutting Speed:
- Cermet inserts provide a superior mirror-like finish due to their lower friction and high thermal stability.
- Carbide inserts deliver excellent performance in both roughing and finishing but may require coatings (such as CVD or PVD) to enhance wear resistance and surface finish.
- Impact Resistance and Toughness:
- Carbide inserts offer higher toughness, making them suitable for heavy roughing, interrupted cuts, and unstable machining conditions.
- Cermet inserts are more brittle and prone to chipping under heavy loads or interrupted cutting but work well under stable cutting conditions.
3. Best Applications for Cermet vs. Carbide Inserts
Choosing between cermet and carbide inserts depends on the machining requirements and material being processed. Below is a general guideline:
| Factor | Cermet Inserts | Carbide Inserts |
|---|---|---|
| Best for | Finishing & Semi-finishing | Roughing & Finishing |
| Cutting Speed | High-speed cutting | Moderate to high speeds |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Very good |
| Toughness | Moderate (brittle) | High (shock-resistant) |
| Interrupted Cutting | Not ideal | Excellent |
| Surface Finish | Superior, smooth finish | Good, depends on coating |
| Best Workpiece Material | Mild steel, alloy steel, cast iron, hardened steel | Stainless steel, cast iron, titanium, superalloys |
4. Cost Considerations
When evaluating cost-effectiveness, it is important to consider both initial tool cost and overall tool life:
- Cermet inserts generally have a longer tool life in finishing operations, reducing the frequency of tool changes.
- Carbide inserts may have a lower initial cost but provide greater flexibility, working effectively across both roughing and finishing operations.
If machining involves continuous finishing and maintaining high surface quality, cermet inserts can reduce costs in the long run. However, for operations involving heavier loads, interrupted cutting, or challenging materials, carbide inserts remain the best choice.
Conclusion
The choice between cermet and carbide inserts depends on the specific machining conditions:
- Cermet inserts are ideal for high-speed finishing with excellent wear resistance and superior surface finish, making them perfect for mild steel and alloy steel.
- Carbide inserts provide better toughness and versatility, making them suitable for a wide range of materials, including stainless steel, titanium, and cast iron, across both roughing and finishing applications.
At Zhuzhou Zhirong Advanced Materials Co., Ltd., we offer a full range of high-performance carbide and cermet cutting inserts designed for precision machining. Our products are made from 100% virgin tungsten carbide powder with advanced CVD and PVD coatings for superior durability and wear resistance.
If you are looking for expert guidance in selecting the best cutting tools for your application, contact us at crystalyuan@zrzhirong.com or visit www.zhirongcarbide.com for more information. We also provide free samples for testing to ensure you receive the best tool performance for your production needs.